When working with Salesforce, you’ll often encounter situations where a record in one object needs to be associated with multiple records in another object, and vice versa. This is where Many-to-Many relationships come into play.
In this blog, we’ll explore:
- What Many-to-Many Relationships are
- Why we need them
- How to implement them using Junction Objects
- A practical real-world example
- Diagram to visualize the relationship
1. What is a Many-to-Many Relationship?
A Many-to-Many relationship means that:
- One record from Object A can be related to multiple records in Object B.
- At the same time, one record from Object B can be related to multiple records in Object A.
👉 Example:
- A Student can enroll in multiple Courses.
- A Course can have multiple Students enrolled.
Clearly, a direct relationship is not enough — we need a bridge between them. That’s where Junction Objects help.
2. Why Do We Need a Junction Object?
Salesforce doesn’t provide a direct “Many-to-Many” relationship type. Instead, we achieve it by creating a Junction Object, which acts as a bridge between two objects.
The Junction Object contains two Master-Detail or Lookup Relationships pointing to the two objects we want to connect.
This way:
- The Junction Object becomes the linking record.
- Each record in the Junction Object represents one association between Object A and Object B.
3. How to Create a Many-to-Many Relationship (Step by Step)
Let’s implement the Student ↔ Course example:
Step 1: Identify the Objects
- Student (Custom Object)
- Course (Custom Object)
Step 2: Create a Junction Object
- Create a custom object called Enrollment (this will act as the bridge).
Step 3: Add Master-Detail Relationships
- On Enrollment, create a Master-Detail relationship to Student.
- On Enrollment, create another Master-Detail relationship to Course.
Step 4: Result
Now:
- A Student can have multiple Enrollments.
- A Course can have multiple Enrollments.
- Each Enrollment record links one Student with one Course.
4. Real-World Example
Here are a few real-world scenarios where Many-to-Many relationships are useful:
- Students ↔ Courses (Education system)
- Doctors ↔ Patients (Healthcare system)
- Products ↔ Orders (E-commerce)
- Employees ↔ Projects (Work management)
5. Diagram of Many-to-Many Relationship
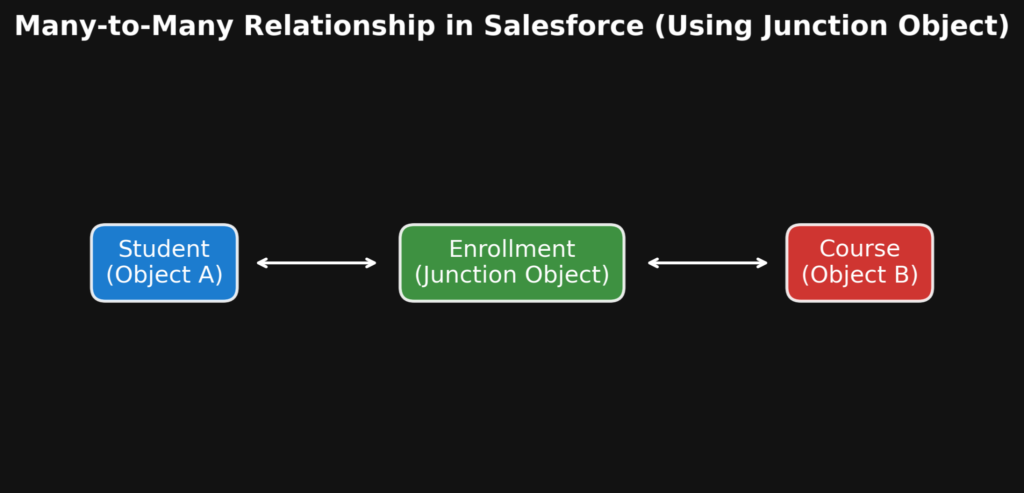
- Student ↔ Enrollment = One-to-Many
- Course ↔ Enrollment = One-to-Many
- Combined → Many-to-Many (Student ↔ Course)
6. Benefits of Using Junction Objects
- Handles complex relationships easily.
- Provides scalability for real-world scenarios.
- Enables custom fields on the junction (like “Enrollment Date” or “Role in Project”).
- Supports reporting across multiple objects.
7. Key Takeaways
- Salesforce doesn’t allow a direct Many-to-Many relationship
- We achieve it using a Junction Object with two Master-Detail or Lookup relationships
- Junction Objects allow us to store additional information about the relationship itself
- Common in real-world use cases like Students & Courses, Employees & Projects, etc.
🔥 Pro Tip:
If you want more flexibility, you can also use Lookup relationships instead of Master-Detail when creating the Junction Object, depending on your business needs.

