When working with Salesforce, one of the most important concepts to understand is how objects relate to each other. Salesforce provides different types of relationships, and among them, the Master-Detail Relationship is one of the most powerful.
In this blog, we’ll break down everything you need to know about Master-Detail Relationships, explain how they work, where they should be used, and show diagrams for easy understanding.
What is a Master-Detail Relationship?
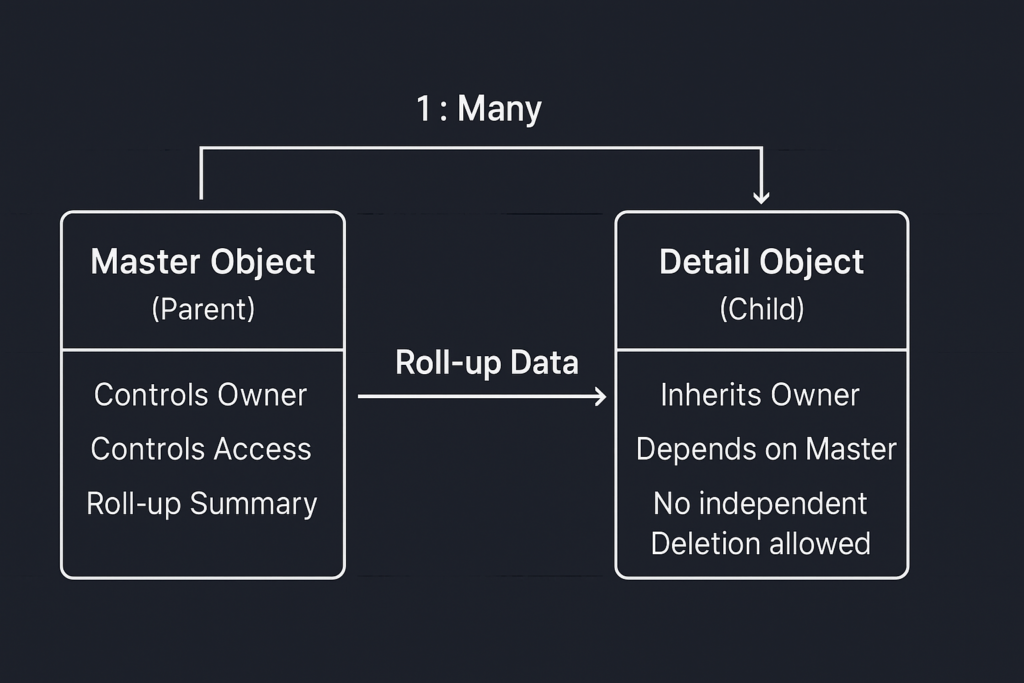
A Master-Detail Relationship in Salesforce is a tight bond between two objects, where one object (the Detail) depends completely on the other object (the Master).
- The Master object controls the behavior of the Detail object.
- The Detail record cannot exist without its Master record.
- If the Master record is deleted, all related Detail records are also deleted (cascade delete).
👉 Think of it as a Parent-Child relationship.
- Parent = Master
- Child = Detail
Key Features of Master-Detail Relationship
- Ownership & Sharing
- The Detail record does not have its own Owner field.
- It inherits the sharing and security settings from the Master record.
- The Detail record does not have its own Owner field.
- Cascade Delete
- If a Master record is deleted, all its associated Detail records are automatically deleted.
- If a Master record is deleted, all its associated Detail records are automatically deleted.
- Roll-Up Summary Fields
- Roll-up summary fields can be created on the Master object to perform calculations (SUM, COUNT, MIN, MAX) on fields from the Detail object.
- Roll-up summary fields can be created on the Master object to perform calculations (SUM, COUNT, MIN, MAX) on fields from the Detail object.
- Mandatory Relationship
- While creating a Detail record, you must always link it to a Master record. It cannot exist independently.
- While creating a Detail record, you must always link it to a Master record. It cannot exist independently.
- Security & Access Control
- The Detail record’s access is always controlled by the Master record’s access.
- The Detail record’s access is always controlled by the Master record’s access.
Diagram for Easy Understanding
Here’s a simple diagram to visualize the relationship:
Example in Salesforce:
- Master: Account
- Detail: Contact (if we set it as Master-Detail)
If the Account is deleted, all its Contacts will also be deleted.
Master-Detail vs. Lookup Relationship
It’s easy to confuse Master-Detail with Lookup Relationship, so let’s compare:
| Feature | Master-Detail | Lookup |
| Dependency | Child must have a Parent | Child may exist without Parent |
| Ownership | Inherited from Master | Independent |
| Deletion Behavior | Cascade delete | No automatic delete |
| Roll-Up Summary | Supported | Not Supported |
| Security & Sharing | Controlled by Master | Independent |
Use Cases of Master-Detail Relationship
- Invoices and Invoice Line Items
- Invoice (Master)
- Line Items (Detail)
- Invoice (Master)
- If the invoice is deleted, all related line items should be deleted too.
- Order and Order Products
- Order (Master)
- Products (Detail)
- Order (Master)
- Products can’t exist without an Order.
- Survey and Survey Responses
- Survey (Master)
- Responses (Detail)
- Survey (Master)
- Each response belongs to a survey and cannot exist on its own.
How to Create a Master-Detail Relationship in Salesforce
- Go to Setup → Object Manager.
- Select the Detail object (the child).
- Go to Fields & Relationships → New.
- Choose Master-Detail Relationship.
- Select the Master object (the parent).
- Set up field-level security, layout, and save.
Things to Keep in Mind
- A custom object can have up to 2 Master-Detail Relationships.
- Converting a Lookup to Master-Detail is possible (if all records have a parent).
- You cannot set a Master-Detail Relationship if the object already has existing records without a parent.
Conclusion
The Master-Detail Relationship is a powerful way to enforce data dependency in Salesforce. It ensures that child records are always tied to a parent record, making data cleaner and more reliable. Features like cascade delete and roll-up summary fields make it one of the most widely used relationships in Salesforce.
👉 Remember:
Use Master-Detail when the child should not exist independently, and use Lookup when the child can stand alone.